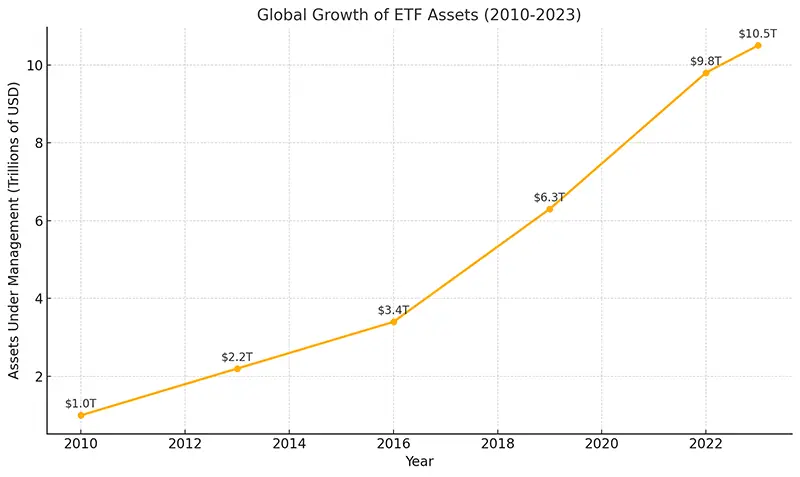
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have become a dominant force in the investment world, transforming how both retail and institutional investors allocate their money. Once a niche financial product, ETFs now hold trillions of dollars in assets globally, offering accessibility, diversification, and cost efficiency. But what led to this explosive growth, and why are ETFs more popular than ever?
The Evolution of ETFs
ETFs first emerged in the early 1990s, with the launch of the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) in 1993. Designed to track the S&P 500 index, SPY offered investors a way to gain diversified market exposure with the flexibility of trading like a stock. Over time, the ETF market expanded to include a wide range of asset classes, including bonds, commodities, real estate, and even thematic investments such as artificial intelligence and clean energy.
Today, there are thousands of ETFs covering nearly every segment of the financial markets, catering to both passive index investors and active traders.
Why ETFs Have Gained Popularity
1. Low Costs & Fee Efficiency
ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. Since most ETFs are passively managed, they avoid the high management fees associated with actively managed mutual funds. With many ETFs charging expense ratios as low as 0.03%, investors can keep more of their returns.
2. Diversification in a Single Trade
One of the biggest advantages of ETFs is their built-in diversification. Investors can buy a single ETF and gain exposure to a broad index, industry, or investment theme. Whether tracking the S&P 500, the Nasdaq, or emerging markets, ETFs make diversification easy and cost-effective.
3. Liquidity and Flexibility
Unlike mutual funds, which are priced once a day, ETFs trade throughout the day like stocks. This allows investors to buy and sell at real-time market prices, use limit orders, and even implement stop-loss strategies.
4. Tax Efficiency
ETFs tend to be more tax-efficient than mutual funds. Thanks to their unique structure, ETFs minimize capital gains distributions, reducing the tax burden for investors.
5. Wide Range of Investment Strategies
The ETF market has expanded beyond basic index tracking. Today, investors can choose from:
- Thematic ETFs (AI, blockchain, ESG investing)
- Leveraged and Inverse ETFs for short-term trading strategies
- Smart Beta ETFs, which combine active and passive management
- Fixed Income ETFs, offering exposure to bonds without direct ownership complexities
The Future of ETFs
The ETF revolution shows no signs of slowing down. Innovations such as actively managed ETFs, cryptocurrency ETFs, and bond laddering ETFs are opening new opportunities for investors. As technology advances and market accessibility improves, ETFs will likely continue reshaping global investing.
With their low costs, transparency, and flexibility, ETFs have democratized investing—providing individuals and institutions alike with powerful tools to build wealth. Whether you’re a long-term investor or a short-term trader, ETFs have something to offer in the modern financial landscape.